Appendix A. CXFS Software Architecture
This appendix discusses the following for administration nodes:
Also see the CXFS MultiOS for CXFS Client-Only Nodes: Installation and Configuration Guide.
The following table lists the CXFS daemons and threads.
 | Note: CXFS shares with XFS
the xfsd kernel threads to push buffered writes to
disk.
|
If you are using a coexecution (of type CXFS and FailSafe
) cluster, see the IRIS FailSafe Version 2 Administrator's Guide, for information
about FailSafe daemons.
Table A-1. CXFS Daemons and Threads
Layer
| Subsystem
| Process
| Description
|
|---|
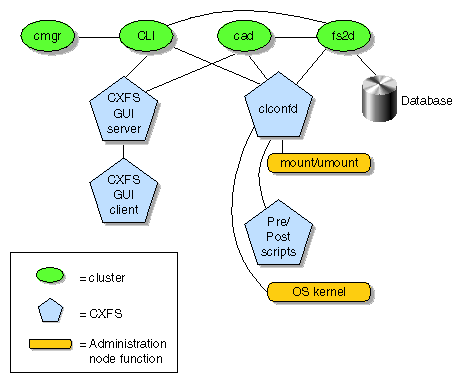
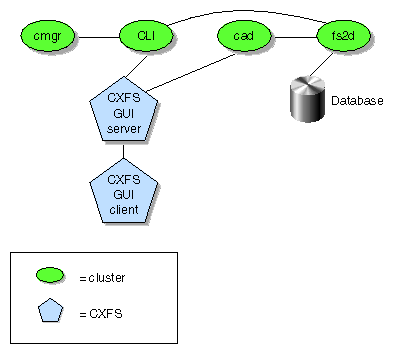
Cluster services (CXFS)
| cluster_services
| clconfd
| CXFS administration cluster configuration
daemon. Reads the cluster configuration from the CDB database and manages
the local kernel's CXFS kernel membership services accordingly.
|
| cxfs_client
| cxfs_client
| CXFS client-only cluster configuration
daemon. Manages the local kernel's CXFS kernel membership services accordingly.
|
Cluster software infrastructure
(cluster administrative processes)
| cluster_admin
| cad
| Cluster administration daemon.
Provides administration services.
|
| cluster_control
| crsd
| Node control daemon. Monitors the
serial connection to other nodes. Has the ability to reset other nodes.
|
|
| cmond
| Daemon that manages all other daemons.
This process starts other processes in all nodes in the cluster and restarts
them on failures.
|
|
| fs2d
| Manages the database and keeps
each copy in synchronization on all nodes in the pool.
|
Kernel Threads
| sthreads
| cmsd
| Manages CXFS kernel membership
and heartbeating. (The CXFS cmsd resides in the kernel;
it differs from the IRIS FailSafe cmsd that resides
in user space.)
|
|
| Recovery
| Manages recovery protocol for node.
|
|
| corpseleader
| Coordinates recovery between nodes.
|
|
| dcshake
| Purges idle CXFS vnodes on the
CXFS client.
|
|
| cxfsd
| Manages sending extent and size
updates from the client to the server. This daemon (which runs on the
CXFS client) takes modified inodes on the client and ships back any size
and unwritten extent changes to the server.
|
| xthreads
| mesgtcprcv
| Reads messages (one per open message
channel).
|
|
| mesgtcpaccept
| Responsible for accepting new connections.
|
|
| mesgtcpdiscovery
| Responsible for monitoring and
discovering other nodes.
|
|
| mesgtcpmulticast
| Responsible for supplying heartbeat.
|
|
|
|
|
The fs2d, clconfd, and
crsd daemons run at real-time priority. However, the
mount and umount commands and scripts executed
by clconfd are run at normal, time-shared priority.
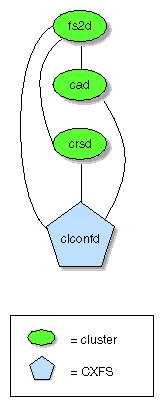
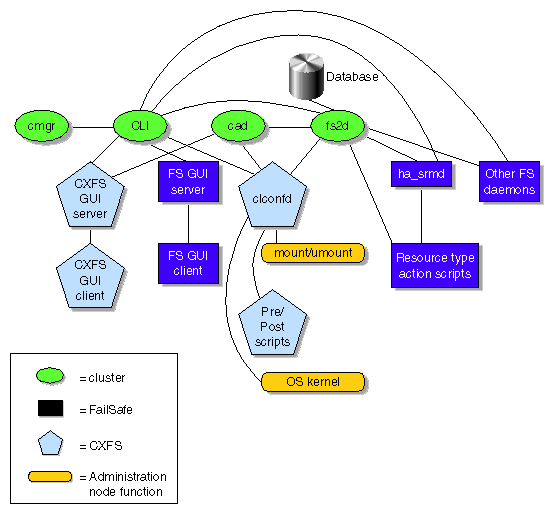
The following figures show communication paths in CXFS.
 | Note: The following figures do not represent the cmond
cluster manager daemon. The purpose of this daemon is to keep
the other daemons running.
|
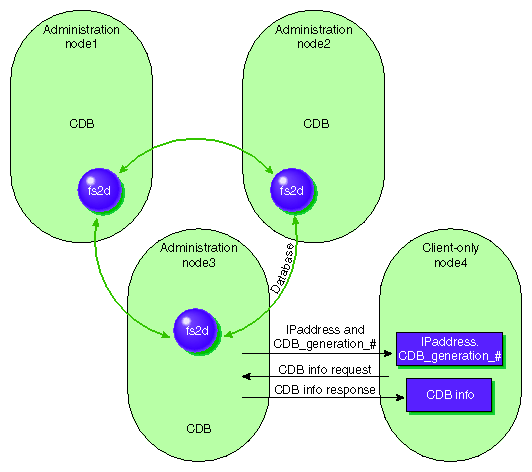
One of the administration nodes running the fs2d
daemon is chosen to periodically multicasts its IP address and the generation
number of the cluster database to each of the client-only nodes. Each
time the database is changed, a new generation number is formed and multicast.
The following figure describes the communication among nodes, using a
Solaris client-only node as an example.
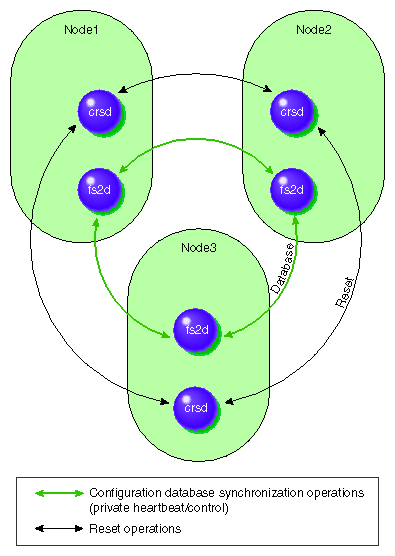
Communication Paths in a Coexecution Cluster
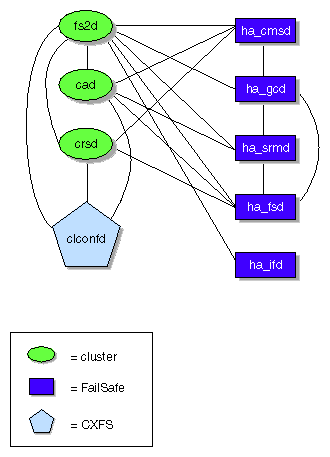
The following figures show the communication paths within one node
in a coexecution cluster running CXFS and IRIS FailSafe.
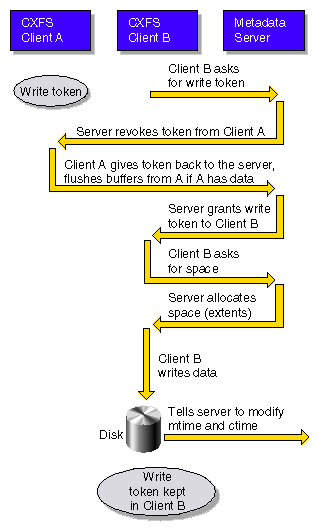
Flow of Metadata for Reads and Writes
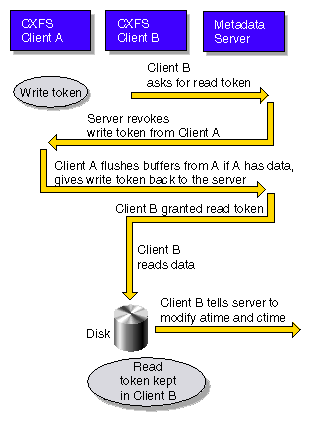
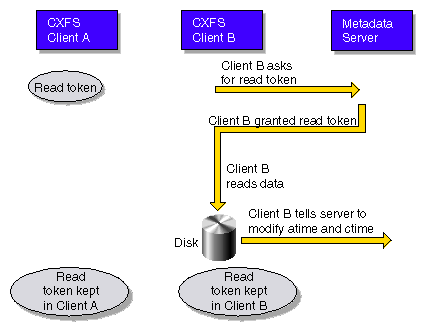
The following figures show examples of metadata flow.
 | Note: A token protects a file. There can be multiple read tokens
for a file at any given time, but only one write token.
|