This chapter summarizes the IRIS ATM application interface calls provided for use by interim local management interface (ILMI) modules. The calls allow an ILMI module to communicate with the IRIS ATM subsystem in retrieving and configuring user network interface (UNI) and management information base (MIB) information. In most situations, these calls do not need to be used by customer-developed applications because the IRIS ATM ILMI software (atmilmid) does the tasks described in this chapter. However, these commands are provided for customers who want to use their own ILMI software for ATM network management. For a summary of these commands, see Table 4-1.
Table 4-1. Summary of ILMI ioctl() Commands
Command | Port State | Description | More Info |
|---|---|---|---|
ATMIOC_GETMIBSTATS | up/dn | Retrieves data from an ATM subsystem for the ATM UNI MIB. | |
ATMIOC_GETPORTINFO | up/dn | Retrieves status and hardware specification information about the device. | |
ATMIOC_GETATMLAYERINFO | up/dn | Retrieves configuration information about the ATM layer of the device. | |
ATMIOC_GETVCCTABLEINFO | up/dn | Retrieves information about all the VCCs currently open on the device. | |
ATMIOC_GETATMADDR | up/dn | Retrieves the device's ATM address. | |
ATMIOC_SETATMADDR | up/dn | Sets (configures) the ATM address for the device. | |
ATMIOC_GETMACADDR |
| Retrieves the device's MAC address. |
The following files must be included in any program using ILMI ATM-specific ioctl() calls:
“sys/atm.h”
“sys/atm_user.h”
The following sections describe each ATM ILMI ioctl() command in detail. The commands are organized alphabetically.
The ATMIOC_GETATMADDR ioctl() command is invoked by an ILMI module to retrieve the ATM address that is currently being used on the device (port).
Use the following format:
ioctl (fd_atm,ATMIOC_GETATMADDR, &address); |
address is an atm_address_t structure.
The argument is a pointer to an empty atm_address_t structure (described in Table 4-2).
If successful, ATMIOC_GETATMADDR returns zero. The out values should be read.
On failure, the ioctl() returns -1 with an error stored in errno. For descriptions of individual errors, see “Errors”.
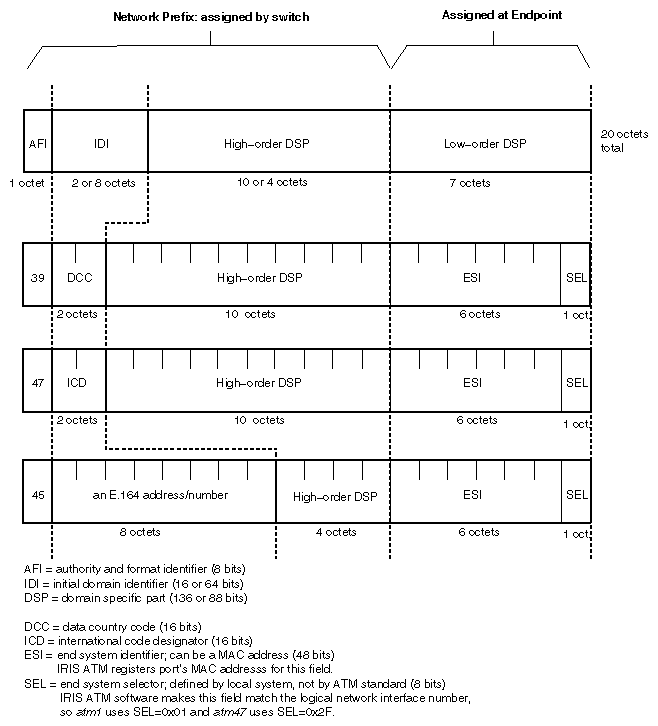
The retrieved ATM address, described in Table 4-2 and Figure 4-1, is copied into the call's argument. The address can be either the ATM network service access point (NSAP) or the native-E.164 format.
Table 4-2. Values Retrieved by the ATMIOC_GETATMADDR Command
Field in atm_address_t | Type | Values |
|---|---|---|
addrType | char | The type of ATM address: 0 = NULLADDR_TYPE 0x02 = NSAP_TYPE 0x11 = E164_TYPE |
addr | union |
|
nsap | char nsap_address_t[20] | See Figure 4-1. |
e164 | e164_address_t | Up to 15 bytes. See the definition in “Relevant Structures”. |
The atm_address_t structure is defined in the sys/atm_user.h file, as follows:
typedef struct atm_address {
char addrType;
union {
nsap_address_t nsap;
e164_address_t e164;
} addr;
} atm_address_t;
typedef char nsap_address_t[20];
typedef struct e164_address {
unsigned char len;
char addr[15];
} e164_address_t; |
The ATMIOC_GETATMLAYERINFO ioctl() command is invoked by an ILMI application to retrieve information about the ATM layer for inclusion in an ATM management information database (MIB).
Use the following format:
ioctl (fd_atm, ATMIOC_GETATMLAYERINFO, &layerinfo); |
layerinfo is an atm_layerinfo_t structure.
If successful, ATMIOC_GETATMLAYERINFO returns zero. The out values should be read.
On failure, the ioctl() returns -1 with an error stored in errno. For descriptions of individual errors, see “Errors”.
The retrieved values are copied to the structure pointed to by the call's argument, described in Table 4-3.
Table 4-3. Values Retrieved by the ATMIOC_GETATMLAYERINFO Command
Field in atm_layerinfo_t | Type | Values |
|---|---|---|
maxVPCs | int | 0 to 0xFF (inclusive) |
maxVCCs | int | 0 to 0xFFFFFF (inclusive) |
configuredVPCs | int | 0 to 0xFF (inclusive) |
configuredVCCs | int | 0 to 0xFFFFFF (inclusive) |
maxVPIbits | int | 0 to 0x8 (inclusive) |
maxVCIbits | int | 0 to 0x20 (inclusive) |
uniType | int | The type of UNI maintained for the port: 1 = PUBLIC_UNI 2 = PRIVATE_UNI 2 |
The atm_layerinfo_t structure is described in Table 4-3, and defined in the sys/atm_user.h file, as follows:
typedef struct {
int maxVPCs;
int maxVCCs;
int configuredVPCs;
int configuredVCCs;
int maxVPIbits;
int maxVCIbits;
int uniType;
} atm_layerinfo_t; |
The ATMIOC_GETMIBSTATS ioctl() command is invoked by an ILMI application to retrieve overall performance information about the UNI for inclusion in an ATM management information database (MIB).
Use the following format:
ioctl (fd_atm, ATMIOC_GETMIBSTATS, &mibstats); |
mibstats is an atm_getmibstats_t structure.
If successful, ATMIOC_GETMIBSTATS returns zero. The out values should be read.
On failure, the ioctl() returns -1 with an error stored in errno. For descriptions of individual errors, see “Errors”.
The retrieved values are copied to the structure pointed to by the call's argument, described in Table 4-4.
Table 4-4. Values Retrieved by the ATMIOC_GETMIBSTATS Command
Field in atm_getmibstats_t | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
receivedCells | int | Total number of ATM cells received. |
droppedReceivedCells | int | Total number of ATM incoming cells that were dropped due to errors or unknown VPI or VCI addresses. |
cellsTransmitted | int | Total number of ATM cells transmitted. |
The atm_getmibstats_t structure is described in Table 4-4, and included below as defined in the sys/atm_user.h file:
typedef struct {
int receivedCells;
int droppedReceivedCells;
int cellsTransmitted;
} atm_getmibstats_t; |
The ATMIOC_GETPORTINFO ioctl() command is invoked by an ILMI application to retrieve information about the hardware for inclusion in an ATM management information database (MIB).
Use the following format:
ioctl (fd_atm, ATMIOC_GETPORTINFO, &portinfo); |
portinfo is an atm_portinfo_t structure.
If successful, ATMIOC_GETPORTINFO returns zero. The out values should be read.
On failure, the ioctl() returns -1 with an error stored in errno. For descriptions of individual errors, see “Errors”.
The retrieved values are copied to the structure pointed to by the call's argument, described in Table 4-5.
Table 4-5. Values Retrieved by the ATMIOC_GETPORTINFO Command
Field in atm_portinfo_t | Type | Values |
|---|---|---|
portOperStatus | int | The status of the port: 1 = OPSTATUS_OTHER 2 = OPSTATUS_INSERVICE 3 = OPSTATUS_OUTOFSERVICE 4 = OPSTATUS_LOOPBACK |
portXmitType | int | The physical layer protocol: 1 = XMITTYPE_UNKNOWN 2 = XMITTYPE_SONETSTS3C 3 = XMITTYPE_DS3 4 = XMITTYPE_4B5B 5 = XMITTYPE_8B10B |
portMediaType | int | The type of transport medium used on the port: 1 = MEDIATYPE_UNKNOWN 2 = MEDIATYPE_COAX 3 = MEDIATYPE_SINGLEMODE 4 = MEDIATYPE_MULTIMODE 5 = MEDIATYPE_SHIELDEDTP 6 = MEDIATYPE_UNSHIELDEDTP |
The atm_portinfo_t structure is described in Table 4-5, and defined in the sys/atm_user.h file, as follows:
typedef struct {
int portOperStatus;
int portXmitType;
int portMediaType;
} atm_portinfo_t; |
The ATMIOC_GETVCCTABLEINFO ioctl() command is invoked by an ILMI module to retrieve information about each open virtual channel (VC). The retrieved listing includes permanent and switched VCs.
Use the following format:
ioctl (fd_atm, ATMIOC_GETVCCTABLEINFO, &sioc); |
sioc is an atmsioc_t structure.
The pointer to sioc identifies an instance of an atmsioc_t structure. The atmsioc_t structure should be set up as summarized in Table 4-6.
Table 4-6. Recommended Values for the Argument of the ATMIOC_GETVCCTABLEINFO Command
Field of atmsioc_t | Recommended Value | Comments |
|---|---|---|
*ptr | Pointer to atm_vcce_t[] | Pointer to location for retrieved information. Upon return, this field is equal to the out value, which is an array of atm_vcce_t structures. |
len | Size of (atm_vcce_t[MAX_FWD_VCS+ MAX_RVS_VCS])
| Maximum possible size of the table. Upon return, this field is equal to the out value, which is the length of the retrieved table. |
If successful, ATMIOC_GETVCCTABLEINFO returns zero. The out values should be read.
On failure, the ioctl() returns -1 with an error stored in errno. For descriptions of individual errors, see “Errors”.
The len field in the argument ( sioc) is updated to contain the actual length of the retrieved data, as described in Table 4-6. The retrieved data is written at the location indicated by the sioc pointer as an array of atm_vcce_t structures. Each table entry is one atm_vcce_t structure, as described in Table 4-7.
Table 4-7. Values Retrieved by the ATMIOC_GETVCCTABLEINFO Command
Field in atm_vcce_t | Type | Values |
|---|---|---|
vpi | int | The VC's virtual path identifier. |
vci | int | The VC's virtual channel identifier. |
xmit_cellrate | struct cellrate_t | The VC's transmit cellrate. See Table 4-8. |
recv_cellrate | struct cellrate_t | The VC's receive cellrate. See Table 4-8. |
xmitQOS | int | The quality of service on the VC's transmit channel. |
recvQOS | int | The quality of service on the VC's receive channel. |
Field | Type | Values |
|---|---|---|
cellrate_type | char | From Table 3-4. |
rate | union | One of the following structures. |
pcr_0_01 | struct |
|
pcr0 | int | Peak cellrate for cell loss priority (CLP) 0, in cells per second |
pcr01 | int | Peak cellrate for CLP 0+1, in cells per second |
pcr_01 | struct |
|
pcr01 | int | Peak cellrate for CLP 0+1, in cells per second |
psb_0_01 | struct |
|
pcr01 | int | Peak cellrate for CLP 0+1, in cells per second |
scr0 | int | Sustainable cellrate for CLP 0, in cells per second |
mbs0 | int | Maximum burst size for CLP 0, in cells per burst |
psb_01 | struct |
|
pcr01 | int | Peak cellrate for CLP 0+1, in cells per second |
scr01 | int | Sustainable cellrate for CLP 0+1, in cells per second |
mbs01 | int | Maximum burst size for CLP 0+1, in cells per burst |
The atm_vcce_t structure is described in Table 4-7, and included below as defined in the sys/atm_user.h file. The cellrate_t structure is described in Table 4-8, and is also defined in the sys/atm_user.h file, as follows:
typedef struct {
int vpi;
int vci;
cellrate_t xmit_cellrate;
cellrate_t recv_cellrate;
int xmitQOS;
int recvQOS;
} atm_vcce_t;
typedef struct {
char cellrate_type;
union {
/* for cellrate_type = CRT_PEAK, CRT_PEAK_TAG */
struct {
int pcr0;
int pcr01;
} pcr_0_01;
/* for cellrate_type = CRT_PEAK_AGG, CRT_BEST_EFFORT */
struct {
int pcr01;
} pcr_01;
/* for cellrate_type = CRT_PSB, CRT_PSB_TAG */
struct {
int pcr01;
int scr0;
int mbs0;
} psb_0_01;
/* for cellrate_type = CRT_PSB_AGG */
struct {
int pcr01;
int scr01;
int mbs01;
} psb_01;
} rate;
} cellrate_t; |
The ATMIOC_SETATMADDR ioctl() command is invoked by an ILMI module to set the ATM address for the port. The program making this call must have super user access privileges.
Use the following format:
ioctl (fd_atm, ATMIOC_SETATMADDR, &address); |
address is an atm_address_t structure.
The atm_address_t structure should be prepared as described in Table 4-9.
Table 4-9. Recommended Values for the Argument of the ATMIOC_SETATMADDR Command
Field in atm_address_t | Type | Values |
|---|---|---|
addrType | char | The type of ATM address: 0 = NULLADDR_TYPE 0x02 = NSAP_TYPE 0x11 = E164_TYPE |
addr | union |
|
nsap | char nsap_address_t[20] | 20 bytes, as illustrated in Figure 4-1. |
e164 | struct e164_address_t |
|
len | u_char | Number of digits in addr array. |
addr | char addr[15] | Up to 15 digits. |
If successful, ATMIOC_SETATMADDR returns zero.
On failure, the ioctl() returns -1 with an error stored in errno. For descriptions of individual errors, see “Errors”.
The atm_address_t structure is defined in the sys/atm_user.h file, as follows:
typedef struct atm_address {
char addrType;
union {
nsap_address_t nsap;
e164_address_t e164;
} addr;
} atm_address_t;
typedef char nsap_address_t[20];
typedef struct e164_address {
unsigned char len;
char addr[15];
} e164_address_t; |