This manual includes the following sections (each is a separate file):
Front matter
Contents
List of Figures
List of Tables
About This Guide, which describes the organization of the manual, references, and typographical conventions
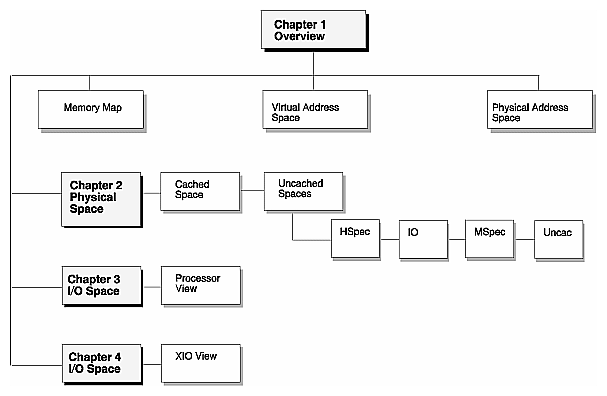
Chapter 1, which describes the Origin™ Family memory map, including the physical and virtual address spaces
Chapter 2, which describes the M Mode physical address space, including the Cached, Hub Special, I/O, Memory Special, and Uncached spaces
Chapter 3, which describes the processor's view of I/O space
Chapter 4, which describes the XIO view of I/O space
Index
The figure on the next page illustrates this organization pictorially.
Much of the explanatory material in this book was taken from the following canons:
Lenoski, Daniel and Weber, Wolf-Dietrich. Scalable Shared-Memory Multiprocessing San Francisco: Morgan Kauffman, 1995.
Hennessy, John and Patterson David. Computer Architecture: A Quantitative Approach San Mateo, California: Morgan Kauffman, 1990
Schimmel, Curt. Unix Systems for Modern Architectures Menlo Park, California: Addison Wesley, 1994
James Laudon's System Specification and Cache Coherence Protocol Specification provided a wealth of information. Both are internal Silicon Graphics® documents.
The following information was also relevant:
Kourosh Gharachorloo, Daniel Lenoski, James Laudon, Phillip Gibbons, Anoop Gupta, and John Hennessy. Memory Consistency and Event Ordering in Scalable Shared-Memory Multiprocessors. Proceedings of the 17th International Symposium on Computer Architecture, pages 15-26, May 1990.
ftp://www-flash.stanford.edu/pub/flash/ISCA90.ps.Z
Kourosh Gharachorloo, Anoop Gupta, and John Hennessy. Revision to Memory Consistency and Event Ordering in Scalable Shared-Memory Multiprocessors. Technical Report CSL-TR-93-568, Computer Systems Laboratory, Stanford University, April 1993.
ftp://www-flash.stanford.edu/pub/flash/ISCA90_rev.ps.Z
Daniel Lenoski, James Laudon, Truman Joe, David Nakahira, Luis Stevens, Anoop Gupta, and John Hennessy. The DASH Prototype: Implementation and Performance. In Proceedings of the 19th International Symposium on Computer Architecture, pages 92-103, Gold Coast, Australia, May 1992.
http://www-flash.stanford.edu/architecture/papers/paperlinks.html
Thanks also to Ben Passarelli, Rick Bahr, Rich Altmaier, Ben Fathi, Ed Reidenbach, Rob Warnock, Jim “Positive-ECL” Smith, Sam Sengupta, Dave Parry, Robert A. dePeyster, Mike Galles, and Luis Stevens.
Finally, thanks to John Mashey (mash@mash.sgi.com) for making himself iteratively available during various emergencies.
is used for emphasis
is used for bits, fields, and registers important from a software perspective (for instance, address bits used by software, programmable registers, etc.)
The following documents provide additional information about the Origin family of systems:
Origin and Onyx2 Theory of Operations Manual, part number 007-3439-nnn
IRIX Device Driver Programmer's Guide, part number 007-0911-nnn
Origin2000 Deskside Server Owner's Guide, part number 007-3453-nnn
Origin2000 Rackmount Owner's Guide, part number 007-3456-nnn
Onyx2 Deskside Workstation Owner's Guide, part number 007-3454-nnn
Origin200 Owner's Guide, part number 007-3415-nnn