This chapter gives information about the system BIOS and tells how to configure the system by changing the settings of the BIOS parameters.
When you receive the system, it will already have been configured by SGI. There is no need to run Setup when starting the computer unless you get a Run Setup message.
The Setup program loads configuration values into the battery-backed, nonvolatile memory called CMOS RAM. This memory area is not part of the system RAM.
 | Note: If you repeatedly receive Run Setup messages, the battery may be bad. In this case, the system cannot retain configuration values in CMOS. Replace the battery or call for support. |
Before you run Setup, make sure that you have saved all open files. The system reboots immediately after you exit Setup.
To enter Setup, simultaneously press the key combination Ctrl+Alt+Esc.
 | Note: You must press Ctrl+Alt+Esc while the system is booting. This key combination does not work at any other time. |
The system supports two Setup utility levels: Basic and Advanced. See Figure 4-1 for the Basic Setup Utility screen and Figure 4-2 for the Advanced Setup Utility screen.
If you are an advanced user, you may want to check the detailed configuration of your system. Detailed system configurations are contained in the Advanced Level. To view the Advanced Level, press F8.
The Key Help Guide (press Alt+H to activate) shows you how to move around the BIOS setup screen:
Use the Up and Down arrow keys to move around the Setup Utility screen.
Use the left and right arrow keys to move to the next page or to return to the previous page if the setup screen has more than one page available.
Use the Page Up, Page Down, +, or - keys to select the options if they are available.
Press Esc to return to the Main menu.

Note: A parameter with an asterisk (*) mark indicates that the parameter appears only when you are in the Advanced Level. Also, grayed items on the screens have fixed settings and are not user-configurable.
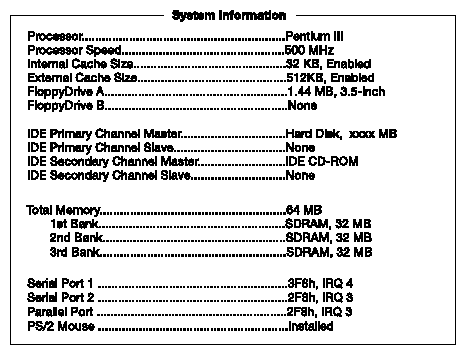
The following screen appears if you select System Information from the Main menu:
Table 4-1 describes the System Information parameters.
Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
Processor | Type of processor currently installed in your system. |
Processor speed | Clock speed of the processor currently installed in your system. |
Internal cache | Total amount of first-level memory or the internal fast-accessed memory size (i.e., the memory integrated into the CPU). |
External cache | Total amount of second-level cache memory size that comes with the CPU. |
Floppy Drive A | System's current diskette drive A settings. |
Floppy Drive B | System's current diskette drive B settings. |
IDE primary channel master | Current configuration of the master IDE device connected to the primary IDE channel. |
IDE primary channel slave | Current configuration of the slave IDE device connected to the primary IDE channel. |
IDE secondary channel master | Current configuration of the master IDE device connected to the secondary IDE channel. |
IDE secondary channel slave | Current configuration of the slave IDE device connected to the secondary IDE channel. |
Total memory | Total amount of onboard memory. The memory size is automatically detected by BIOS during the power-on self-test. If you install additional memory, the system automatically adjusts this parameter to display the new memory size. |
1st/2nd/3rd bank | Type and size of DRAM installed in DIMM sockets 1, 2, and 3. The None setting indicates that there is no DRAM installed. For the location of the DIMM sockets, see Figure 3-1 . |
Serial port 1 | Serial port 1 address and IRQ setting. |
Serial port 2 | Serial port 2 address and IRQ setting. |
Parallel port | Parallel port address and IRQ setting. |
PS/2 mouse | Pointing device installation settings. Displays None if no pointing device is installed. |
The Product Information screen contains general data about the system, such as the product name, serial number, BIOS version, etc. This information is necessary for troubleshooting (and may be required when asking for technical support).
Figure 4-4 shows the Product Information screen.
Table 4-2 describes the Product Information parameters.
Table 4-2. Product Information
Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
Product name | Official name of the system |
System S/N | System's serial number |
Main board ID | Main board's identification number |
Main board S/N | Main board's serial number |
System BIOS version | Version of the BIOS utility |
DMI BIOS version | Version of the DMI BIOS |
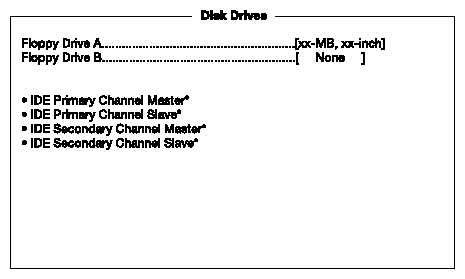
Select Disk Drives to input configuration values for disk drives.
The following screen shows the Disk Drives menu:
 | Note: A parameter with an asterisk (*) mark indicates that the parameter appears only when you are in the Advanced Level. See “Entering Setup”. |
Table 4-3 describes the Disk Drives parameters. Settings in boldface are the default and suggested parameter settings.
Table 4-3. Disk Drives Parameters
Parameter | Description | Option |
|---|---|---|
Floppy drive A and B | Selects the floppy disk drive type. | 1.44 MB, 3.5-inch None 360 KB, 5.25-inch 1.2 MB, 5.25-inch 720 KB, 3.5-inch 2.88 MB, 3.5-inch |
IDE primary channel master and slave IDE Secondary channel master and slave | This item lets you select the IDE hard disk parameters that your system supports. Auto enables BIOS to automatically detect the parameters of installed HDD during the POST (power-on self-test). If you prefer to enter HDD parameters manually, select User. Select None if no HDD is connected to the system. The IDE CD-ROM is always automatically detected. | Auto User None |
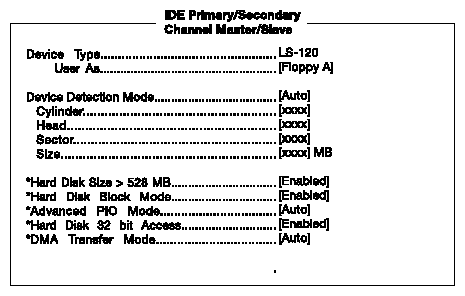
The following screen appears if you select any of the IDE Drive parameters:
Table 4-4 describes the parameters in this screen. Settings in boldface are the default and suggested parameter settings.
Table 4-4. IDE Drive Parameters
Parameter | Description | Option |
|---|---|---|
Device Type | Indicates a hard disk type device. |
|
Used As | Specifies the designated drive name for the device type. | Floppy A Floppy B Hard disk |
Device Detection Mode | Lets you specify the type of hard disk installed in your system. If you want the BIOS to automatically configure your hard disk, select Auto. If you know your hard disk type, you can select User, and enter the setting manually. | Auto User None |
Cylinder | Specifies the number of cylinders of your hard disk, This can only be modified if Device Detection Mode is set to Manual. If Device Detection Mode is set to Auto, this parameter will be set by the system. | User Input |
Head | Specifies the number of heads of your hard disk. This can only be modified if Device Detection Mode is set to Manual. If Device Detection Mode is set to Auto, this parameter will be set by the system | User Input |
Sector | Specifies the number of sectors of your hard disk. This can only be modified if Device Detection Mode is set to Manual. If Device Detection Mode is set to Auto, this parameter will be set by the system | User Input |
Size | Specifies the size of your hard disk, in MB. This can only be modified if Device Detection Mode is set to Manual. If Device Detection Mode is set to Auto, this parameter will be set by the system | User Input |
Hard disk size > 528 MB | When set to Auto, the BIOS utility automatically detects if the installed hard disk supports the function. If supported, it allows you to use a hard disk with a capacity of more than 528 MB. This is made possible through the Logical Block Address (LBA) mode translation. However, this enhanced IDE feature works only under DOS, Windows 3.x, Windows 95, and Windows NT 3.5 and above. Other operating systems require this parameter to be set to Disabled. | Enabled Disabled |
Hard disk block mode | Enhances disk performance depending on the hard disk in use. If you set this parameter to Auto, the BIOS utility automatically detects if the installed hard disk drive supports the Block Mode function. If supported, it allows data transfer in blocks (multiple sectors) at a rate of 256 bytes per cycle. | Auto Disabled |
Advanced PIO mode | When set to Auto, the BIOS utility automatically detects if the installed hard disk supports the function. If supported, it allows for faster data recovery and read/write timing that reduces hard disk activity time. This results in better hard disk performance. | Auto Disabled |
Hard disk 32 bit access | Improves system performance by allowing the use of the 32-bit hard disk access. This enhanced IDE feature works only under DOS, Windows 3.x, Windows 95, Windows NT, and Novell NetWare. If your software or hard disk does not support this function, set this parameter to Disabled. | Enabled Disabled |
DMA transfer mode | The Ultra DMA and Multi-DMA modes enhance hard disk performance by increasing the transfer rate. However, besides enabling these features in the BIOS Setup, both the Ultra DMA and Multi-DMA modes require the DMA driver to be loaded. By setting this parameter to Auto, BIOS automatically sets the appropriate DMA mode for your hard disk. | Auto Disabled |
The Onboard Peripheral Configuration option allows you to configure the onboard communication ports and the onboard devices. Selecting this option displays the following screen:
Table 4-5 describes the Onboard Peripherals parameters. Settings in boldface are the default and suggested parameter settings.
Table 4-5. Onboard Peripherals Parameters
Parameter | Description | Option |
|---|---|---|
Serial port 1 and 2 | Enables or disables the serial port | Enabled Disabled |
Base address | Sets the I/O base address of the serial port | 3F8h 2F8h 3E8h 2E8h |
IRQ | Sets the IRQ (interrupt request) channel of the serial port | 4 11 |
Parallel port | Enables or disables the parallel port | Enabled Disabled |
Base address | Sets the I/O base address of the parallel port. | 378h 278h 3BCh |
IRQ | Sets the interrupt request (IRQ) channel of the parallel port Note: If you install an add-on card that has a parallel port whose address conflicts with the onboard parallel port, a warning appears on the screen. Check the parallel port address of the add-on card and change the address to one that does not conflict. | 7 5 |
Operation mode | Selects the operation mode of the parallel port. Standard Parallel Port (Standard) – allows normal speed, one-way operation. Standard and Bidirectional (Bidirectional) – allows normal speed operation in a two-way mode. Enhanced Parallel Port (EPP) – allows bidirectional parallel port operation at maximum speed. Extended Capabilities Port (ECP) – allows parallel port to operate in bidirectional mode and at a speed higher than the maximum data transfer rate. | Bi-directional EPP ECP Standard |
ECP DMA channel | Sets the DMA channel of the parallel port when the parallel operation mode is set to ECP. | 1 3 |
Floppy disk controller | Sets the control level of the diskette drive. | Normal Disabled Write Protect All Sectors Write Protect Boot Sector |
IDE controller | Sets the control level of the IDE drive. | Normal Disabled Write Protect All Sectors Write Protect Boot Sector |
PS/2 mouse controller | Enables or disables the onboard PS/2 mouse controller. | Enabled Disabled |
USB host controller | Enables or disable the on board USB controller. | Enabled Disabled |
USB legacy mode | When enabled, allows you to use a USB keyboard in DOS. Set this to Disabled to deactivate the USB keyboard function in DOS. | Disabled Enabled |
The Power Management menu allows you to configure the system power-management feature.
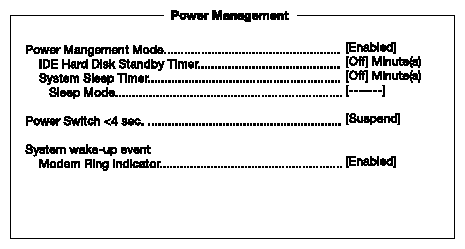
The following screen shows the Power Management parameters and their default settings:
Table 4-6 describes the Power Management parameters. Settings in boldface are the default and suggested parameter settings.
Table 4-6. Power Management Parameters
Parameter | Description | Option |
|---|---|---|
Power management mode | Allows you to reduce power consumption. When this parameter is set to Enabled, you can configure the IDE hard disk and system timers. Setting it to Disabled deactivates the power-management feature and its timers. | Enabled Disabled |
IDE hard disk standby timer | Allows the hard disk to enter standby mode after inactivity of 1 to 15 minutes, depending on your setting. When you access the hard disk again, allow 3 to 5 seconds (depending on the hard disk) for the disk to return to normal speed. Set this parameter to Off if your hard disk does not support this function. | Off 1 minute 15 minutes |
System sleep timer | This parameter sets the system to the lowest power-saving mode after a specified period of inactivity. Any keyboard or mouse action or any activity detected from the IRQ channels resumes system operation. | Off On |
Sleep mode | Lets you specify the power-saving mode that the system will enter after a specified period of inactivity. This parameter becomes configurable only if the system sleep timer is on. Any keyboard or mouse action, or any enabled monitored activities occurring through the IRQ channels resume system operation. | Standby Suspend |
Power switch < 4 sec. | When set to Power off, the system automatically turns off when the power switch is pressed for less than 4 seconds. When set to Suspend, the system enters the suspend mode when pressed for less than 4 seconds. | Suspend Power off |
System wake-up event | The system wake-up event allows the system to resume operation when the modem ring indicator is enabled. |
|
Modem ring indicator | When Enabled, any fax/modem activity wakes up the system from suspend mode. | Enabled Disabled |
The Boot Options selection allows you to specify your preferred setting for bootup.
The following screen appears if you select Boot Options from the Basic Configuration menu:
 | Note: A parameter with an asterisk (*) mark indicates that the parameter appears only when you are in the Advanced Level. See “Entering Setup”. |
Table 4-7 describes the Boot Options parameters. Settings in boldface are the default and suggested parameter settings.
Table 4-7. Boot Options Parameters
Parameter | Description | Option |
|---|---|---|
Boot Sequence | This parameter allows you to specify the boot search sequence during POST. - 1st. The system checks this drive first. - 2nd. The system then checks this drive if it can not boot from the 1st specified drive. - 3rd. If the 1st and 2nd searches fail, it boots from this drive. BIOS will display an error message if the drive specified is not bootable. |
|
Primary display adapter | Setting this parameter to Auto enables the onboard video controller. Normally, the onboard video controller is considered as the primary display adapter. If you installed a video card into your system, you need to disable the onboard VGA; otherwise, the video card will not function. To do this, simply set this parameter to Disabled. | Onboard Disabled |
Fast boot | Allows the system to boot faster by skipping some POST routines. | Disabled Enabled |
Silent boot | Enables or disables the Silent Boot function. When set to Enabled, BIOS is in graphical mode and displays only an identification logo during POST and while booting. After booting, the screen displays the operating system prompt (such as DOS) or logo (such as Windows 95). If any error occurs while booting, the system automatically switches to the text mode. Even if your setting is Enabled, you may also switch to the text mode while booting by pressing the Delete key when you see the “Press DELETE key to enter setup” message on the screen. When set to Disabled, BIOS is in the conventional text mode where you see the system initialization details on the screen. | Enabled Disabled |
Num lock after boot | Allows you to activate the Num Lock function upon booting. | Enabled Disabled |
Memory test | When set to Enabled, this parameter allows the system to perform a RAM test during the POST routine. When set to Disabled, the system detects only the memory size and bypasses the test routine. | Enabled Disabled |
The real-time clock keeps the system date and time. After setting the date and time, you do not need to enter them every time you turn on the system. As long as the internal battery remains good (approximately 7 years) and connected, the clock continues to keep the date and time accurately even when the power is off.
Table 4-8 describes the Date and Time parameters.
Table 4-8. Date and Time Parameters
Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
Date | Set the date following the weekday-month-day-year format. Valid values for weekday, month, day, and year are: Weekday: Sun, Mon, Tue, Wed, Thu, Fri, Sat Month: Jan, Feb, Mar, Apr, May, Jun, Jul, Day: 1 to 31 Year: 1980 to 2079 |
Time | Set the time following the hour-minute-second format. Valid values for hour, minute, and second are: Hour: 00 to 23 Minute: 00 to 59 Second: 00 to 59 |
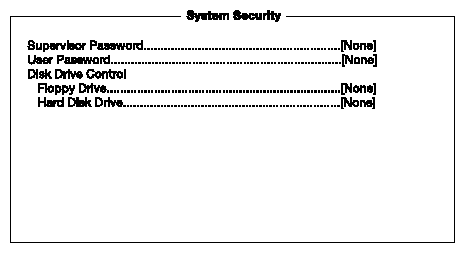
The Setup program has a number of security features to prevent unauthorized access to the system and its data.
The following screen appears if you select System Security from the Setup Utility screen:
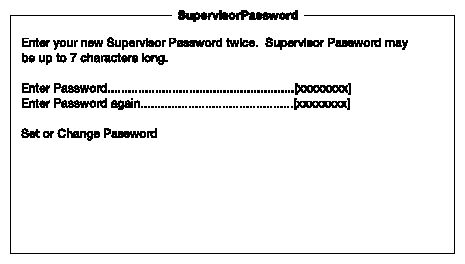
The Supervisor Password prevents unauthorized access to the BIOS utility.
Enable the Supervisor Password parameter in the System Security menu by pressing the left or right arrow keys. The Supervisor Password window appears:
Type a password in the Enter Password field. The password may consist of up to seven characters.
Press the Enter key. Retype your password in the Enter Password Again field to verify your first entry.
Highlight Set or Change Password and press the Enter key.
Press the Esc key to return to the System Security menu and then press the Esc key again to exit Setup. The Exit Setup screen appears:
Choose Yes to save your settings and exit the Setup Utility. Your password will be saved to CMOS.
The next time you want to enter the BIOS utility, you must key in your Supervisor password.
To remove your Supervisor Password:
Disable the Supervisor Password parameter in the System Security menu by pressing the left or right arrow key to select None.
Press the Esc key to return to the System Security menu and then press the Esc key again to exit Setup. The Exit Setup screen appears:
Choose Yes to save your settings and exit Setup Utility. Your previous password will be removed from CMOS.
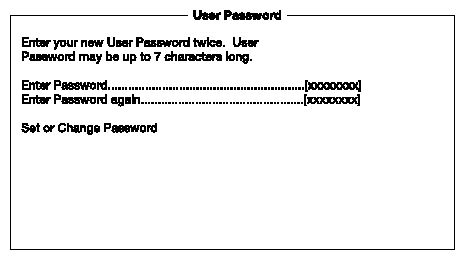
The User Password secures your system against unauthorized use. Once you set this password, you have to type it whenever you boot the system. To set this password, enter the Setup Utility, select System Security, and then highlight the User Password parameter. Follow the procedure used in “Supervisor Password”.
The disk drive control features allow you to control the floppy drive or the hard disk drive boot function to prevent loading operating systems or other programs from a certain drive while the other drives are operational (under DOS mode only).
Table 4-9 describes the Disk Drive Control settings.
Setting | Description |
|---|---|
Normal | Floppy drive or hard disk drive functions normally |
Write Protect All Sectors | Disables the write function on all sectors |
Write Protect Boot Sectors | Disables the write function only on the boot sector |
The Advanced Options configuration menu allows you to configure the system memory, PCI device settings, and CPU frequency. To view the Advanced Options screen, press F8.
 | Note: If you are not a qualified technician, to avoid damaging the system do not change any settings under Advanced Options. |
The following screen shows the Advanced Options parameters:
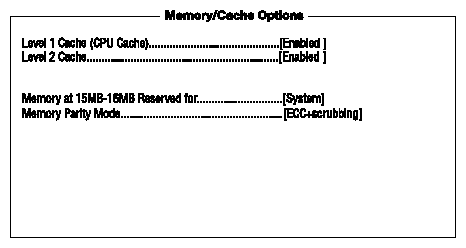
The Memory/Cache Options allow you to configure the advanced system memory functions.
Table 4-10 describes the Memory/Cache Options parameters screen. Settings in boldface are the default and suggested parameter settings.
Table 4-10. Memory/Cache Options Parameters
Parameter | Description | Option |
|---|---|---|
Level 1 cache | This parameter enables or disables the first-level or internal memory, that is, the memory integrated into the CPU. | Enabled Disabled |
Level 2 cache | This parameter enables or disables the second-level cache memory. The second-level cache is incorporated into the CPU module. | Enabled Disabled |
Memory at 15MB-16MB Reserved for | To prevent memory address conflicts between the system and expansion boards, reserve this memory range for the use of either the system or an expansion board. | System Expansion board |
Memory Parity Mode | Enables or disables the ECC (Error Checking and Correction) feature. The ECC feature enables BIOS to detect and correct data errors. Disable this parameter if you want to disregard the function. | ECC+scrubbing Disabled |
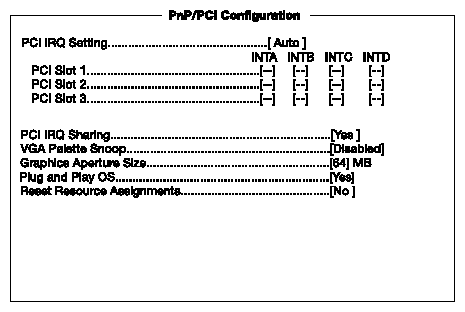
The PnP/PCI Options allows you to specify the settings for your plug-and-play (PnP) PCI devices. Selecting this option displays the following screen:
Table 4-11 describes the PnP/PCI Options parameters. Settings in boldface are the default and suggested parameter settings.
Table 4-11. PnP/PCI Options Parameters
Parameter | Description | Option |
|---|---|---|
PCI IRQ sharing | Select Auto to let the BIOS automatically configure the plug-and-play (PnP) devices installed on your system. Otherwise, select Manual. Note: Refer to your manual for technical information about the PCI card. | Auto Manual |
PCI slot 1 to 3 | When you set the PCI IRQ Setting parameter to Auto, these parameters specify the auto-assigned interrupt for each of the PCI devices. If you set the PCI IRQ Setting parameter to Manual, you need to specify the interrupt that you want to assign for each PCI device installed in your system. | User input |
PCI IRQ sharing | Setting this parameter to Yes allows you to assign the same IRQ to two different devices. To disable the feature, select No. Note: If there are no IRQs available to assign for the remaining device function, we recommend that you enable this parameter. | Yes No |
VGA palette snoop | This parameter permits you to use the palette snooping feature if you installed more than one VGA card in the system. The VGA palette snoop function allows the control palette register (CPR) to manage and update the VGA RAMDAC (Digital Analog Converter, a color data storage) of each VGA card installed in the system. The snooping process lets the CPR send a signal to all the VGA cards so that they can update their individual RAMDACs. The signal goes through the cards continuously until all RAMDAC data has been updated. This allows the display of multiple images on the screen. Note: Some VGA cards have required settings for this feature. Check your VGA card manual before setting this parameter. | Disabled Enabled |
Graphics aperture size | This parameter determines the effective size of the graphics aperture. The graphics aperture is the address range that the AGP video and the CPU use to manage graphical objects. The lowest setting is 8 MB and the highest is 256 MB. | User input |
Plug and play OS | When this parameter is set to Yes, BIOS initializes only PnP boot devices such as SCSI cards. When set to No, BIOS initializes all PnP boot and non-boot devices such as sound cards. Note: Set this parameter to Yes only if your operating system is Windows 95/98. | Yes No |
Reset resource assignments | Set this parameter to Yes to avoid IRQ conflict when installing non-PnP cards. This clears all resource assignments and allows BIOS to reassign resources to all installed PnP devices the next time the system boots. After clearing the resource data, the parameter resets to No. | No Yes |
Use the Load Default Settings option to load the default settings for the optimized system configuration. When you load the default settings, some of the parameters are grayed-out with their fixed settings. These grayed parameters are not user-configurable.
The following dialog box appears when you select Load Default Settings from the Main menu:
Select Yes to load the default settings.
Select No to ignore the message and return to the BIOS utility.
Use the Abort Settings Change option to disregard your changes to the BIOS and reload your previous settings.
The following dialog box appears when you select Abort Settings Change from the Main menu:
Select Yes to disregard your changes and reload your previous settings. After reloading, the Main menu appears on your screen.
Select No to ignore the message and return to the BIOS utility
Examine the system configuration values. When you are satisfied that all the values are correct, write them down. Store the recorded values in a safe place. In the future, if the battery loses power or the CMOS chip is damaged, you will know what values to enter when you rerun Setup.
Press the Esc key to leave the Setup utility. The following dialog box appears:
Use the arrow keys to select your response. Press the Enter key.
If you made any changes to the Setup utility, the following dialog box appears:
Use the arrow keys to select your response. Select Yes to save the changes in CMOS. Select No to retain the old configuration values. Press the Enter key to exit.