This chapter describes the function and physical components of the C-brick in the following sections:
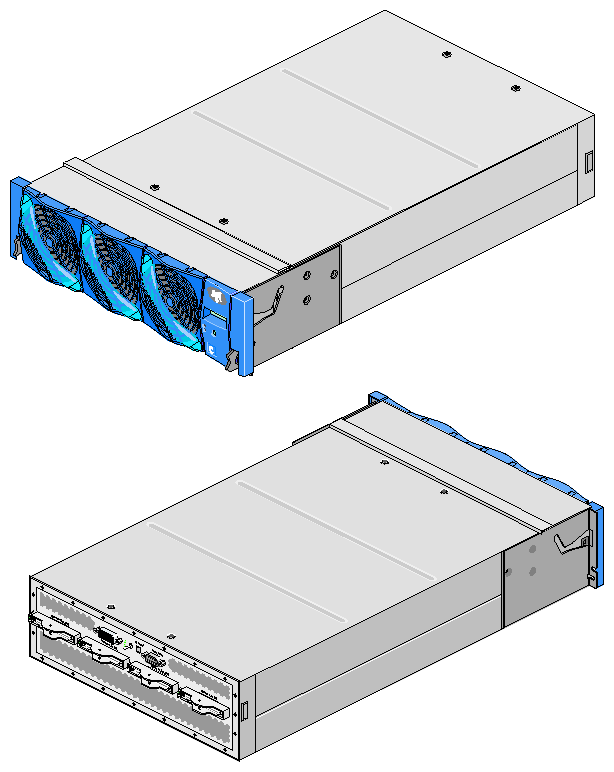
The C-brick is a 3U-high enclosure that contains the compute and memory functionality for the SGI Altix 3000 system. Figure 5-1 shows front and rear views of the C-brick.
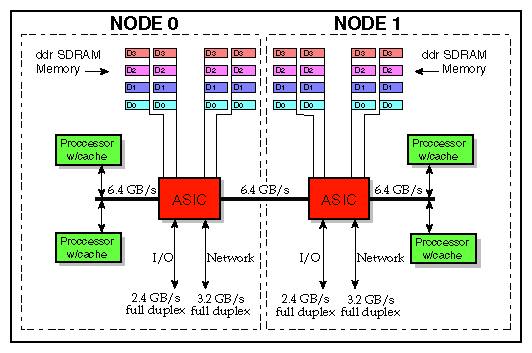
The C-brick is divided into two separate nodes that are connected internally by a high-speed NUMAlink channel. Each node has two 64-bit RISC processors and 16 memory DIMM slots connected to a custom-designed application-specific integrated circuit (ASIC). This ASIC is the heart of the C-brick, and it provides an intelligent interface between the processors, memory, network fabric, and peripheral I/O.
The C-brick has the following features:
Four 64-bit RISC processors (two processors per node)
Four 1.5- or 3.0-MB secondary caches (one per processor)
32 memory DIMM slots (16 slots per node)
Two internal 3.2-GB/s (each direction) NUMAlink channels (one per node)
Two external 1.6-GB/s (each direction) NUMAlink channels (one per node)
Two 1.2-GB/s (each direction) Xtown2 I/O channels (one per node)
One USB port for system controller support
One serial console port
One L1 controller and LCD display
Three hot-pluggable fans
Figure 5-2 shows a block diagram of the C-brick.
This section describes the external components located on the front and rear panels of the C-brick.
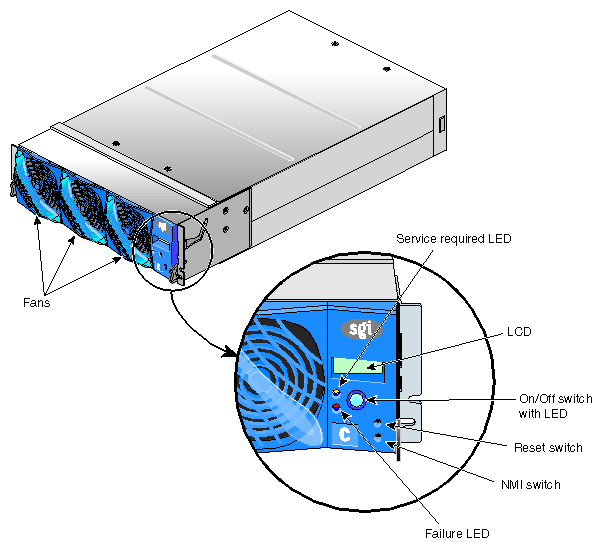
The C-brick contains the following front panel items (see Figure 5-3):
Three hot-pluggable fans.
L1 controller display. The display is a 55.7 mm X 32mm backlit liquid crystal display (LCD) that displays system messages. It will display two lines with a maximum of 12 characters on each line.
On/Off switch with LED. Press this switch to turn on the C-brick internal components. You can also turn these on at a system console. If your system has an L2 controller, you can turn these on at the L2 controller touch display.
L1 controller switches and LEDs:
On/Off LED. This LED illuminates green when the C-brick internal components are on and turns off when they are off.
Service required LED. This LED illuminates orange to indicate that an item is broken or not operating properly (for example, a fan is off), but the C-brick is still operating.
Failure LED. This LED illuminates red to indicate that a system failure has occurred and the C-brick system is down.
Reset switch. Press this switch to reset the internal processors of the C-brick. All register values will be reset to their default states and the operating system will be rebooted. (See the non-maskable interrupt [NMI] to perform a reset without losing the register data.)
Non-maskable interrupt [NMI] switch. Press this switch to force the C-brick into power-on diagnostics (POD) mode. The PROM saves the register state for each CPU. On the next reboot, the operating system retrieves the information from PROM and logs it in the system log. SGI service personnel can also perform an error dump or other maintenance action before rebooting the partition. The NMI command is necessary to troubleshoot a system.
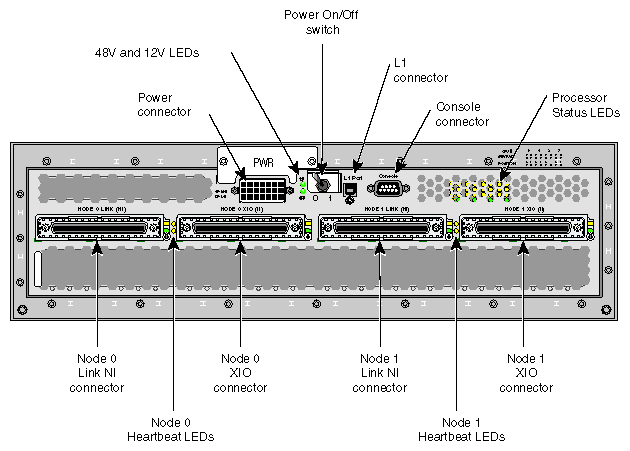
The C-brick has the following rear panel items (see Figure 5-4):
Power switch. Move the power switch to the I position to power on the L1 controller within the C-brick, and to the 0 position to power off the L1 controller. Powering on the L1 controller illuminates the 12-VDC LED green.
PWR (power) connector. This connects the C-brick to the power bay, to provide 12-VDC and 48-VDC power to the C-brick.
48-VDC and 12-VDC LEDs. The power switch must be in the ON (I) position for these LEDs to be on. The 12-VDC LED illuminates green when the L1 controller is powered on and operating, and the 48-VDC LED illuminates green when the rest of the C-brick internal components are powered on and operating. You can power on the internal components by pressing the On/Off switch (brick reset button) on the L1 controller panel.
Node 0 and Node 1 LINK (NI - Network Interface) connectors. These Xtown2 connectors connect the C-brick to an R-brick or to another C-brick. These are connected with a NUMAlink cable at 1.6 GB/s in each direction.
Heartbeat LEDs. The four heartbeat LEDs turn on and off at a preset rate when the Linux operating system is running. The heartbeat LEDs indicate that the processor is functioning and can process an interrupt from the operating system. The LEDs for each node are arranged in pairs. The lower LED represents the processor 0 heartbeat, and the upper LED represents the processor 1 heartbeat.
Node 0 and Node 1 XIO (II - I/O Interface) connectors. These Xtown2 connectors connect a C-brick to an I/O-brick (IX-brick or PX-brick). These are connected with a NUMAlink cable at 1.2 GB/s in each direction.
Console connector. This is an RS-232 serial port (console and diagnostic port) that connects the L1 controller within a C-brick to a system console. The C-brick L1 controller communicates with a system console through the console connector, which provides a serial bus that uses the standard RS-232 protocol.
L1 port connector. This universal serial bus (USB) connector connects the L1 controller within a C-brick to the L2 controller on the rack enclosure for systems with no router.
Processor status LEDs. The 32 processor status LEDs (8 for each processor) are used by SGI service engineers for diagnostic purposes.
Link and XIO connector LEDs. Each connector has an LED that illuminates yellow and an LED that illuminates green. One LED illuminates yellow to indicate that both the C-brick and the brick to which it is connected are powered on. The other LED illuminates green when the link between the C-brick and the other brick is established.
The node electronics, L1 controller, and power regulators are contained on a half-panel power board. The two SHUBs, four processors, and four processor power pods are housed on a second half-panel printed circuit board (PCB). This second PCB also provides connections for the four memory daughter cards. Note: The internal components of the C-brick can be serviced only by trained SGI technicians.
Four 64-bit Intel Itanium 2 processors with secondary cache are mounted on a a half panel printed circuit board.
See “I/O Port Specifications” in Appendix A for pinout specifications for the non-proprietary connectors on the C-brick.
See Table 5-1 for configurable items in the C-brick.
The C-brick has the following restrictions:
All processors within the C-brick must be the same frequency; however, C-bricks within a partition or system can have different processor speeds.
All processor revisions must be the same within a processor node.
The processor revisions of CPUs between processor nodes can be no greater than n+1.
All memory DIMMs within a memory bank must be the same speed, capacity, and use the same chip technology.
Different logical banks within a C-brick can have different DIMM capacities and chip technologies.
Memory DIMMs must be added in groups of eight DIMMs.
Table 5-2 lists the technical specifications of the C-brick.
Table 5-2. C-brick Technical Specifications
Characteristic | Specification |
|---|---|
Height | 5.06 in. (133.35 mm) |
Width | 17.19 in. (436.63 mm) |
Depth | 27.80 in. (706.12 mm) |
Weight | 55 lb (24.95 kg) |
Input power | 48 VDC (~ 1125 W) |
Table 5-3 lists the specifications of the C-brick ports.
Table 5-3. C-brick Port Specifications
Port | Quantity | Specification |
|---|---|---|
Node 0 (NI) | 1 | 1.6 GB/s each direction |
Node 1 (NI) | 1 | 1.6 GB/s each direction |
Node 0 (II) | 1 | 1.2 GB/s each direction |
Node 1 (II) | 1 | 1.2 GB/s each direction |
Console | 1 | 115 Kbits/s |
L1 | 1 | 12 Mbits/s |